Product Syndication
Intershop Commerce Management provides two mechanisms for distributing products across channels: product sharing and product syndication. For a general introduction, see Product Sharing vs. Product Syndication.
With product syndication, sales channels can derive master products from parent sales or partner organizations. The master products are actually copied to the channel repositories. Copied (or derived) products are sometimes also called "offers".
Products are stored in product repositories.
-
Each sales or partner organization can set up a master product repository. From the master repositories, products can be derived into the available channel repositories.
-
Channel repositories are defined in the context of a channel. Each channel has a channel product repository. The channel repository contains the products to be made available to customers or partners.
Using master and channel repositories, products can flow down the demand chain: from the sales organization to customers and sales partners, from the sales partners to indirect resellers, and so on.
Product syndication involves the following general workflow:
-
Define Attribute Mapping Rules
Product syndication requires the mapping of attributes (standard product attributes, catalog assignments, prices, etc.) of the original source product into attributes of a target product (offer). Attribute mapping is governed by product data mapping rules.
-
Select Products for Syndication
Products can be derived in different ways and from different repositories, depending on whether you derive products into a master repository or a channel repository.
-
Manage Synchronization
Synchronization ensures that derived products remain synchronized with their sources in case the sources are updated.
For details about executing syndication processes, see Product Syndication and Synchronization.
Attribute Mapping Rules
Product syndication requires the mapping of attributes (standard product attributes, catalog assignments, prices, etc.) of the original source product into attributes of the derived product.
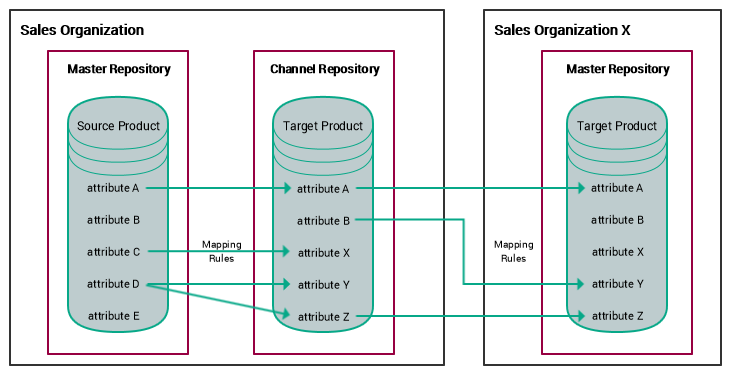
The simplest mapping operation is to copy the value of a source product attribute into the same attribute of the target product. A more complex operation is to copy a source product attribute into a different attribute of the target product or, even more complex, to manipulate the attribute value before storing it into the target product, such as calculating a margin on a product price or translate the name of a product into another language.
Different rule sets can be defined depending on the source repository from which products are derived. Each rule set enables you to specify the following:
| Data | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Defines whether product ID's for seller, supplier and manufacturer are copied, and if so, whether they are copied as-is, or with a prefix and/or suffix added. |
| Attributes | Defines (for each attribute) whether the attribute is to be copied as-is, or to be mapped onto a different attribute. Attributes for which no mapping rule is defined are not mapped at all. |
| Attribute Groups | This option makes it possible to automatically synchronize all attributes that belong to a certain attribute group. With this option, attribute values are always copied as-is. |
| Category | Defines whether category assignments are preserved. This option is only applicable in case products are syndicated from a master repository into a channel repository. This option also presumes that the master catalogs to which the category assignments relate have been shared to the respective channel. |
| Classifications | Defines whether assignments to classification systems (such as ecl@ss and UN/SPSC) are preserved. This option is only applicable in case the classification system is available for the current repository as well. |
| Attachments | Defines whether attachments to a product (such as data sheets) are preserved. Attachments can be copied or be defined as link to the original data source. |
| Assignments | Defines whether product bundle, retail set and variation assignments are preserved when syndication takes place. |
| Price | Price can be copied as-is, or be mapped to a different currency using a certain exchange rate. Note that for each target currency, only one rule can be defined. In addition, you can define a surcharge or discount that applies when copying or mapping prices. |
| Links | Defines whether settings for product links of the original data source are preserved. Note that links to other products are preserved only in case the products in question have been syndicated as well. |
Synchronization
Synchronization ensures that derived products remain synchronized with their source products in case the sources are updated. You can define individually for each source repository whether synchronization should be triggered manually in Intershop Commerce Management, or via an automated job at regular intervals.
Synchronization can be set to:
-
Apply to all products in the source repository, regardless of whether source data have changed (Synchronize All).
This option is used, for example, in case product data mapping rules have changed, requiring a synchronization over the entire set of products.
-
Apply to only those products in the source repository which have been modified.
This option is used to apply changes in the source repository to the syndicated products.
You can use the product history to track updated, changed or added products in accessible source repository. In addition, differences between source and derived products are automatically tracked by the system.
The synchronization process runs as a batch process. Updates are applied automatically.
